 |
| January 05, 2021 | Volume 17 Issue 01 |
Electrical/Electronic News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Conductive Brush Ring overcomes current leakage in EV powertrains
 SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
Learn more.
Intro to reed switches, magnets, magnetic fields
 This brief introductory video on the DigiKey site offers tips for engineers designing with reed switches. Dr. Stephen Day, Ph.D. from Coto Technology gives a solid overview on reed switches -- complete with real-world application examples -- and a detailed explanation of how they react to magnetic fields.
This brief introductory video on the DigiKey site offers tips for engineers designing with reed switches. Dr. Stephen Day, Ph.D. from Coto Technology gives a solid overview on reed switches -- complete with real-world application examples -- and a detailed explanation of how they react to magnetic fields.
View the video.
Bi-color LEDs to light up your designs
 Created with engineers and OEMs in mind, SpectraBright Series SMD RGB and Bi-Color LEDs from Visual Communi-cations Company (VCC) deliver efficiency, design flexibility, and control for devices in a range of industries, including mil-aero, automated guided vehicles, EV charging stations, industrial, telecom, IoT/smart home, and medical. These 50,000-hr bi-color and RGB options save money and space on the HMI, communicating two or three operating modes in a single component.
Created with engineers and OEMs in mind, SpectraBright Series SMD RGB and Bi-Color LEDs from Visual Communi-cations Company (VCC) deliver efficiency, design flexibility, and control for devices in a range of industries, including mil-aero, automated guided vehicles, EV charging stations, industrial, telecom, IoT/smart home, and medical. These 50,000-hr bi-color and RGB options save money and space on the HMI, communicating two or three operating modes in a single component.
Learn more.
All about slip rings: How they work and their uses
 Rotary Systems has put together a really nice basic primer on slip rings -- electrical collectors that carry a current from a stationary wire into a rotating device. Common uses are for power, proximity switches, strain gauges, video, and Ethernet signal transmission. This introduction also covers how to specify, assembly types, and interface requirements. Rotary Systems also manufactures rotary unions for fluid applications.
Rotary Systems has put together a really nice basic primer on slip rings -- electrical collectors that carry a current from a stationary wire into a rotating device. Common uses are for power, proximity switches, strain gauges, video, and Ethernet signal transmission. This introduction also covers how to specify, assembly types, and interface requirements. Rotary Systems also manufactures rotary unions for fluid applications.
Read the overview.
Seifert thermoelectric coolers from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added new high-quality and efficient stainless steel Seifert 340 BTU/H thermoelectric coolers with 120-V and 230-V power options. Thermoelectric coolers from Seifert use the Peltier Effect to create a temperature difference between the internal and ambient heat sinks, making internal air cooler while dissipating heat into the external environment. Fans assist the convective heat transfer from the heat sinks, which are optimized for maximum flow.
Automation-Direct has added new high-quality and efficient stainless steel Seifert 340 BTU/H thermoelectric coolers with 120-V and 230-V power options. Thermoelectric coolers from Seifert use the Peltier Effect to create a temperature difference between the internal and ambient heat sinks, making internal air cooler while dissipating heat into the external environment. Fans assist the convective heat transfer from the heat sinks, which are optimized for maximum flow.
Learn more.
EMI shielding honeycomb air vent panel design
 Learn from the engineering experts at Parker how honeycomb air vent panels are used to help cool electronics with airflow while maintaining electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Topics include: design features, cell size and thickness, platings and coatings, and a stacked design called OMNI CELL construction. These vents can be incorporated into enclosures where EMI radiation and susceptibility is a concern or where heat dissipation is necessary. Lots of good info.
Learn from the engineering experts at Parker how honeycomb air vent panels are used to help cool electronics with airflow while maintaining electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Topics include: design features, cell size and thickness, platings and coatings, and a stacked design called OMNI CELL construction. These vents can be incorporated into enclosures where EMI radiation and susceptibility is a concern or where heat dissipation is necessary. Lots of good info.
Read the Parker blog.
What is 3D-MID? Molded parts with integrated electronics from HARTING
 3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
View the video.
Loss-free conversion of 3D/CAD data
 CT CoreTech-nologie has further developed its state-of-the-art CAD converter 3D_Evolution and is now introducing native interfaces for reading Solidedge and writing Nx and Solidworks files. It supports a wide range of formats such as Catia, Nx, Creo, Solidworks, Solidedge, Inventor, Step, and Jt, facilitating smooth interoperability between different systems and collaboration for engineers and designers in development environments with different CAD systems.
CT CoreTech-nologie has further developed its state-of-the-art CAD converter 3D_Evolution and is now introducing native interfaces for reading Solidedge and writing Nx and Solidworks files. It supports a wide range of formats such as Catia, Nx, Creo, Solidworks, Solidedge, Inventor, Step, and Jt, facilitating smooth interoperability between different systems and collaboration for engineers and designers in development environments with different CAD systems.
Learn more.
Top 5 reasons for solder joint failure
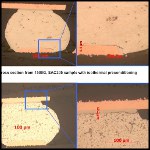 Solder joint reliability is often a pain point in the design of an electronic system. According to Tyler Ferris at ANSYS, a wide variety of factors affect joint reliability, and any one of them can drastically reduce joint lifetime. Properly identifying and mitigating potential causes during the design and manufacturing process can prevent costly and difficult-to-solve problems later in a product lifecycle.
Solder joint reliability is often a pain point in the design of an electronic system. According to Tyler Ferris at ANSYS, a wide variety of factors affect joint reliability, and any one of them can drastically reduce joint lifetime. Properly identifying and mitigating potential causes during the design and manufacturing process can prevent costly and difficult-to-solve problems later in a product lifecycle.
Read this informative ANSYS blog.
Advanced overtemp detection for EV battery packs
 Littelfuse has introduced TTape, a ground-breaking over-temperature detection platform designed to transform the management of Li-ion battery systems. TTape helps vehicle systems monitor and manage premature cell aging effectively while reducing the risks associated with thermal runaway incidents. This solution is ideally suited for a wide range of applications, including automotive EV/HEVs, commercial vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Littelfuse has introduced TTape, a ground-breaking over-temperature detection platform designed to transform the management of Li-ion battery systems. TTape helps vehicle systems monitor and manage premature cell aging effectively while reducing the risks associated with thermal runaway incidents. This solution is ideally suited for a wide range of applications, including automotive EV/HEVs, commercial vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Learn more.
Benchtop ionizer for hands-free static elimination
 EXAIR's Varistat Benchtop Ionizer is the latest solution for neutralizing static on charged surfaces in industrial settings. Using ionizing technology, the Varistat provides a hands-free solution that requires no compressed air. Easily mounted on benchtops or machines, it is manually adjustable and perfect for processes needing comprehensive coverage such as part assembly, web cleaning, printing, and more.
EXAIR's Varistat Benchtop Ionizer is the latest solution for neutralizing static on charged surfaces in industrial settings. Using ionizing technology, the Varistat provides a hands-free solution that requires no compressed air. Easily mounted on benchtops or machines, it is manually adjustable and perfect for processes needing comprehensive coverage such as part assembly, web cleaning, printing, and more.
Learn more.
LED light bars from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct adds CCEA TRACK-ALPHA-PRO series LED light bars to expand their offering of industrial LED fixtures. Their rugged industrial-grade anodized aluminum construction makes TRACKALPHA-PRO ideal for use with medium to large-size industrial machine tools and for use in wet environments. These 120 VAC-rated, high-power LED lights provide intense, uniform lighting, with up to a 4,600-lumen output (100 lumens per watt). They come with a standard bracket mount that allows for angle adjustments. Optional TACLIP mounts (sold separately) provide for extra sturdy, vibration-resistant installations.
Automation-Direct adds CCEA TRACK-ALPHA-PRO series LED light bars to expand their offering of industrial LED fixtures. Their rugged industrial-grade anodized aluminum construction makes TRACKALPHA-PRO ideal for use with medium to large-size industrial machine tools and for use in wet environments. These 120 VAC-rated, high-power LED lights provide intense, uniform lighting, with up to a 4,600-lumen output (100 lumens per watt). They come with a standard bracket mount that allows for angle adjustments. Optional TACLIP mounts (sold separately) provide for extra sturdy, vibration-resistant installations.
Learn more.
World's first metalens fisheye camera
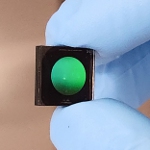 2Pi Optics has begun commercial-ization of the first fisheye camera based on the company's proprietary metalens technology -- a breakthrough for electronics design engineers and product managers striving to miniaturize the tiny digital cameras used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), AR/VR, UAVs, robotics, and other industrial applications. This camera can operate at different wavelengths -- from visible, to near IR, to longer IR -- and is claimed to "outperform conventional refractive, wide-FOV optics in all areas: size, weight, performance, and cost."
2Pi Optics has begun commercial-ization of the first fisheye camera based on the company's proprietary metalens technology -- a breakthrough for electronics design engineers and product managers striving to miniaturize the tiny digital cameras used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), AR/VR, UAVs, robotics, and other industrial applications. This camera can operate at different wavelengths -- from visible, to near IR, to longer IR -- and is claimed to "outperform conventional refractive, wide-FOV optics in all areas: size, weight, performance, and cost."
Learn more.
Orbex offers two fiber optic rotary joint solutions
 Orbex Group announces its 700 Series of fiber optic rotary joint (FORJ) assemblies, supporting either single or multi-mode operation ideal for high-speed digital transmission over long distances. Wavelengths available are 1,310 or 1,550 nm. Applications include marine cable reels, wind turbines, robotics, and high-def video transmission. Both options feature an outer diameter of 7 mm for installation in tight spaces. Construction includes a stainless steel housing.
Orbex Group announces its 700 Series of fiber optic rotary joint (FORJ) assemblies, supporting either single or multi-mode operation ideal for high-speed digital transmission over long distances. Wavelengths available are 1,310 or 1,550 nm. Applications include marine cable reels, wind turbines, robotics, and high-def video transmission. Both options feature an outer diameter of 7 mm for installation in tight spaces. Construction includes a stainless steel housing.
Learn more.
Mini tunnel magneto-resistance effect sensors
 Littelfuse has released its highly anticipated 54100 and 54140 mini Tunnel Magneto-Resistance (TMR) effect sensors, offering unmatched sensitivity and power efficiency. The key differentiator is their remarkable sensitivity and 100x improvement in power efficiency compared to Hall Effect sensors. They are well suited for applications in position and limit sensing, RPM measurement, brushless DC motor commutation, and more in various markets including appliances, home and building automation, and the industrial sectors.
Littelfuse has released its highly anticipated 54100 and 54140 mini Tunnel Magneto-Resistance (TMR) effect sensors, offering unmatched sensitivity and power efficiency. The key differentiator is their remarkable sensitivity and 100x improvement in power efficiency compared to Hall Effect sensors. They are well suited for applications in position and limit sensing, RPM measurement, brushless DC motor commutation, and more in various markets including appliances, home and building automation, and the industrial sectors.
Learn more.
Can ultraviolet communication help transform Army networks?

Army researchers are studying the detectability of ultraviolet communication systems in a bid to deliver more secure military networks. [Photo: K. Kassens]
Of ever-increasing concern for operating a tactical communications network is the possibility that a sophisticated adversary may detect friendly transmissions. Army researchers have developed an analysis framework that enables the rigorous study of the detectability of ultraviolet communication systems, providing the insights needed to deliver the requirements of future, more secure Army networks.
In particular, ultraviolet communication has unique propagation characteristics that not only allow for a novel non-line-of-sight optical link, but also may be harder for an adversary to detect.
Building off an experimentally validated channel modeling, channel simulations, and detection and estimation theory, the developed framework enables the evaluation of tradeoffs associated with different design choices and the manner of operation of ultraviolet communication systems, said Dr. Robert Drost of the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command's Army Research Laboratory.
"While many techniques have been proposed to decrease the detectability of conventional radio-frequency, or RF, communications, the increased atmospheric absorption of deep-ultraviolet wavelengths implies that ultraviolet communication, or UVC, has a natural low-probability-of-detection, or LPD, characteristic," Drost said. "In order to fully take advantage of this characteristic, a rigorous understanding of the LPD properties of UVC is needed."
In particular, Drost said, such understanding is essential for optimizing the design and operation of UVC systems and networks and for predicting the quality of the LPD property in a given scenario, such as using UVC to securely network a command post that has an estimate of the direction and distance to the adversary.
Without such a predictive capability, he said, users would lack the guidance needed to know the extent and limit of their detectability, and this lack of awareness would substantially limit the usefulness of the LPD capability.
The researchers, including Drs. Mike Weisman, Fikadu Dagefu, Terrence Moore, and Drost from CCDC ARL and Dr. Hakan Arlsan, Oak Ridge Associated Universities postdoctoral fellow at the lab, demonstrated this by applying their framework to produce a number of key insights regarding the LPD characteristics of UVC, including:
- LPD capability is relatively insensitive to a number of system and channel properties, which is important for the robustness of the LPD property;
- Adversarial line-of-sight detection of a non-line-of-sight communication link is not as significant of a concern as one might fear;
- Perhaps counter to intuition, steering of a UVC transmitter does not appear to be an effective detection-mitigation strategy in many cases; and
- A line-of-sight UVC link provides non-line-of-sight standoff distances that are commensurate with the communication range.
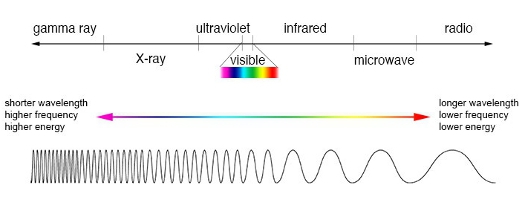
Comparison of wavelength, frequency, and energy for the electromagnetic spectrum. [Credit: NASA's Imagine the Universe]
Prior modeling and experimental research has demonstrated that UVC signals attenuate dramatically at long distance, leading to the hypothesis that UVC has a fundamental LPD property, Drost said. However, there has been little effort to rigorously and precisely quantify this property in terms of the detectability of a communication signal.
"Our work provides a framework enabling the study of the fundamental limits of detectability for an ultraviolet communication system meeting desired communication performance requirements," Drost said.
Although this research is focused on longer-term applications, he said, it is addressing the Army Modernization Priority on Networks by developing the fundamental understanding of a novel communications capability, with a goal of providing the Soldier with network connectivity despite challenging environments that include adversarial activity.
Another key effort involves the experimental characterization, exploration, and demonstration of this technology in a practical network using ARL's Common Sensor Radio, a sophisticated mesh-networking radio designed to provide robust and energy-efficient networking.
This research supports the laboratory's FREEDOM (Foundational Research for Electronic Warfare in Multi-Domain Operations) Essential Research Program goal of studying the integration of low-signature communications technologies with advanced camouflage and decoy techniques.
According to Drost, the work is also an on-ramp to studying how ultraviolet communications and other communications modalities, including conventional radio-frequency communications, can operate together in a seamless and autonomous heterogeneous network, which the researchers believe is needed in order to fully realize the benefits of individual novel communication technologies.
As they make continued progress on these fundamental research questions, the researchers will continue to work closely with their transition partner at the CCDC C5ISR (Command, Control, Computers, Communications, Cyber, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) Center to push ultraviolet communications toward nearer-term transition to the warfighter.
This work is featured in a paper, "Analysis of the low-probability-of-detection characteristics of ultraviolet communications," which the Optical Society's peer-reviewed journal, Optics Express, recently accepted for publication.
Source: U.S. Army CCDC Army Research Laboratory
Published September 2020
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
